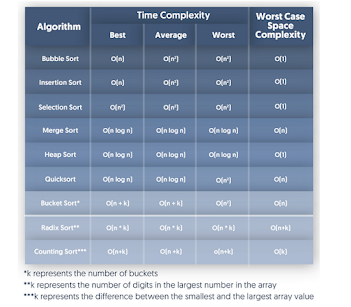
Time complexity
Quick sort Worst Case = O(n2) Average case and best case: O(n log n)
Merge sort Worst case = Average Case = Best Case = O(n log n)
Heap Sort Worst case = Average Case = Best Case = O(n log n)
Space complexity
Quick sort Worst Case = O(n) Average case and best case: O( log n)
This happens when the pivot element’s correct position in the
partitioned array is in the middle every time. The size of subarrays
will be half the size of the original array. In this case, the recursive
tree’s size will be O(log n).
Merge sort Worst case = O(n) Average Case = Best Case = O( log n)
Since we use an auxiliary array of size at most n to store the merged subarray, the space complexity is O(n).
Heap sort O(1) Doesnt require extra space